Raspberry Pie cm0
CM0 Dev Board
Utilizes the same RP3 SIP chipset as the Raspberry Pi Zero 2W
Primarily positioned for low-power, low-cost industrial computing
According to online descriptions, it consumes approximately 3W under full load and around 1W under idle, requiring only a 5V power supply.
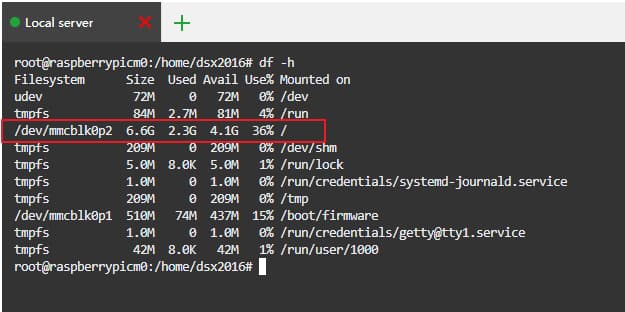
It has 512MB of RAM, with optional onboard 8GB or 16GB eMMC storage.

Use cases
Taking the 8GB onboard eMMC storage CM0 dev kit as an example
Its low power consumption and 24-hour stability make it suitable for message gateways, network proxies, data acquisition, screen panels, and machine vision (OpenCV, etc.).
Network Proxy:
- frp network proxy allows other devices to use it for unified proxy tunneling for SSH, HTTP, etc.
- WireGuard network proxy allows remote devices to securely join a company or intranet, enabling remote access to local area network resources, such as home NAS, printers, Raspberry Pi, and cameras.
Smart Home:
- Message notifications, such as those triggered by the NTFY algorithm, can be sent when temperatures exceed a threshold, high concentrations of gas pollution are detected, or a fire warning is issued.
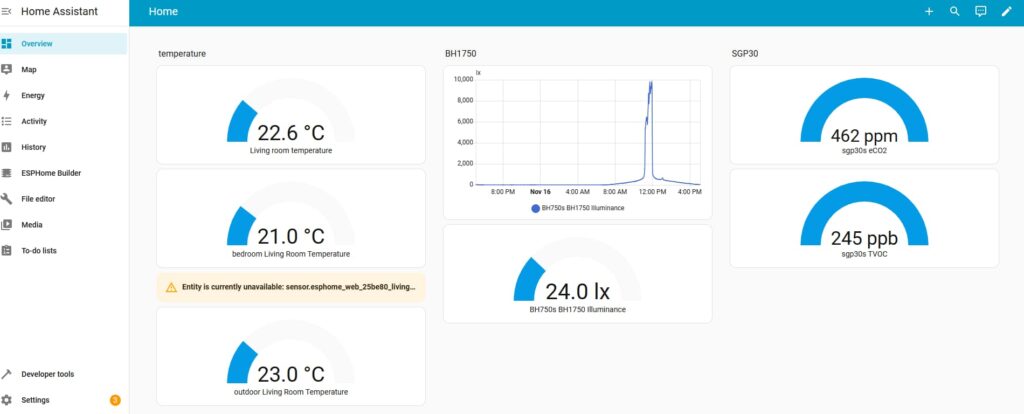
- MQTT (Mosquitto) is used for data reporting and receiving, such as MQTT reporting of sensor data (e.g., to Home Assistant) and MQTT reception of data for display on screen panels, showing charts such as temperature and humidity.
- Visual programming, Node-RED, is primarily used for the Internet of Things (IoT), automation, and process control.
Web server:
- Static websites, like lighttpd, can display static HTML. Screen panels can show charts and dashboards for temperature and humidity, and the HTML can be customized. Touchscreens can display status information, receive MQTT data, and provide interactive functions such as controlling lights.
Information panel:
- The small size, low power consumption, and stable industrial design of the cm0 are ideal for information display panels, such as TFT, OLED, and touch screens.
Machine vision:
- When paired with cameras and OpenCV, it can perform object recognition, facial recognition, license plate recognition, and posture recognition. In smart home scenarios, it can identify water meters, electricity meters, and gas meters, recognize their digits, upload them to Home Assistant, record and notify users of changes in the values.
In industrial scenarios such as sensor data acquisition and reporting, and control of industrial equipment (e.g., small motors, switches, pumps, etc.): CM0 connects to the control board/sensor via GPIO/serial port (UART/SPI/I2C), and works with a watchdog timer to ensure stable system restarts and monitor key personnel.
Other scenarios (ad filtering):
- dnsmasq supports DNS caching and DHCP distribution, and when used with Pi-hole, it can easily achieve ad blocking.
- Pi-hole, ad blocking
- adguardhome, ad blocker
The above three are mainly for home use.
docker
The projects listed in this article are all open-source and free, require low memory (average 10-30MB of memory), and can be deployed using Docker.
Raspberry Pi cm0 has the ecosystem of Raspberry Pi software systems, and it’s ready to use out of the box with Raspberry Pi OS (based on Debian).
We have tested and installed Docker and Docker Compose, as well as installed and run the frp agent (network agent) using Docker.
I have configured SSH remote access to my home devices and public network access to the Home Assistant web panel and Home Assistant app.
Tips
The Raspberry Pi CM0 has 512MB of RAM and a 1GHz CPU.
It is suitable for Raspberry Pi OS Lite (server) systems, but not for desktop versions, and is insufficient to support the installation of Home Assistant and PVE.
If it’s an onboard eMMC, then the TF card slot cannot be used. However, eMMC is fast, durable, and reliable, making it suitable for lightweight SQLite data and message gateways and network proxies.
Advantages and features of CM0
| Features | Advantages of agricultural/urban scenarios |
|---|---|
| Low power consumption | Solar-powered and unattended |
| Small size | Easy to embed in sensor nodes or robots |
| GPIO rich | Directly drive sensors, relays, and actuators |
| Support edge computing | Sensor data can be processed locally, reducing network load. |
| Low cost | Large-scale deployment is possible |
In agriculture, this can be achieved through smart irrigation, greenhouse monitoring, crop growth data collection, and drones/robots.
In cities, smart streetlights, smart landscaping, environmental monitoring, and smart parking can be implemented.
Makers and DIY testers can design information panels, network boxes, and drones, etc.